The world of cryptocurrencies can seem complex, filled with jargon and new concepts. If you’re looking to buy, sell, or trade digital currencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, or Dogecoin, you’ll inevitably encounter crypto exchanges. But what exactly are they, and how do they function? Think of a crypto exchange as a digital marketplace, similar to a stock exchange, but specifically for cryptocurrencies. It’s a platform where buyers and sellers can connect to trade different digital assets for other cryptocurrencies or traditional fiat currencies (like INR, USD, EUR).
What Exactly is a Crypto Exchange?
At its core, a crypto exchange provides the infrastructure and tools for users to:
- Buy Cryptocurrencies: Purchase digital assets using fiat currencies or other cryptocurrencies.
- Sell Cryptocurrencies: Exchange their digital assets for fiat currencies or other cryptocurrencies.
- Trade Cryptocurrencies: Speculate on the price movements of different cryptocurrencies by trading them against each other.
These platforms act as intermediaries, facilitating transactions and ensuring a smooth trading experience for their users. They typically earn revenue through transaction fees charged on trades.
How Does a Crypto Exchange Work?
While the specifics can vary between different exchanges, the fundamental workings are quite similar:
1. Account Creation and Verification:
To start trading on a crypto exchange, you’ll first need to create an account. This usually involves providing personal information, such as your name, email address, and date of birth. Most reputable exchanges also require Know Your Customer (KYC) verification, where you’ll need to upload identification documents like your Aadhaar card, PAN card, or passport. This is done to comply with regulatory requirements and prevent illicit activities.
2. Funding Your Account:
Once your account is verified, you need to deposit funds to start trading. Exchanges typically offer various funding methods, including:
- Fiat Currency Deposits: You can deposit INR (since we are in Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India), USD, EUR, or other supported fiat currencies via bank transfers, UPI, credit/debit cards, or other payment gateways.
- Cryptocurrency Deposits: If you already own cryptocurrencies, you can transfer them from your external crypto wallet to your exchange wallet. Each exchange provides unique deposit addresses for different cryptocurrencies.
3. Placing Orders:
With funds in your account, you can now start placing orders to buy or sell cryptocurrencies. The two main types of orders you’ll encounter are:
- Market Order: This is an order to buy or sell a cryptocurrency at the best available current price. Market orders are executed quickly but you might not get the exact price you were hoping for due to price fluctuations.
- Limit Order: This allows you to set a specific price at which you want to buy or sell a cryptocurrency. Your order will only be executed if the market price reaches your specified limit. This gives you more control over the price but there’s no guarantee your order will be filled.
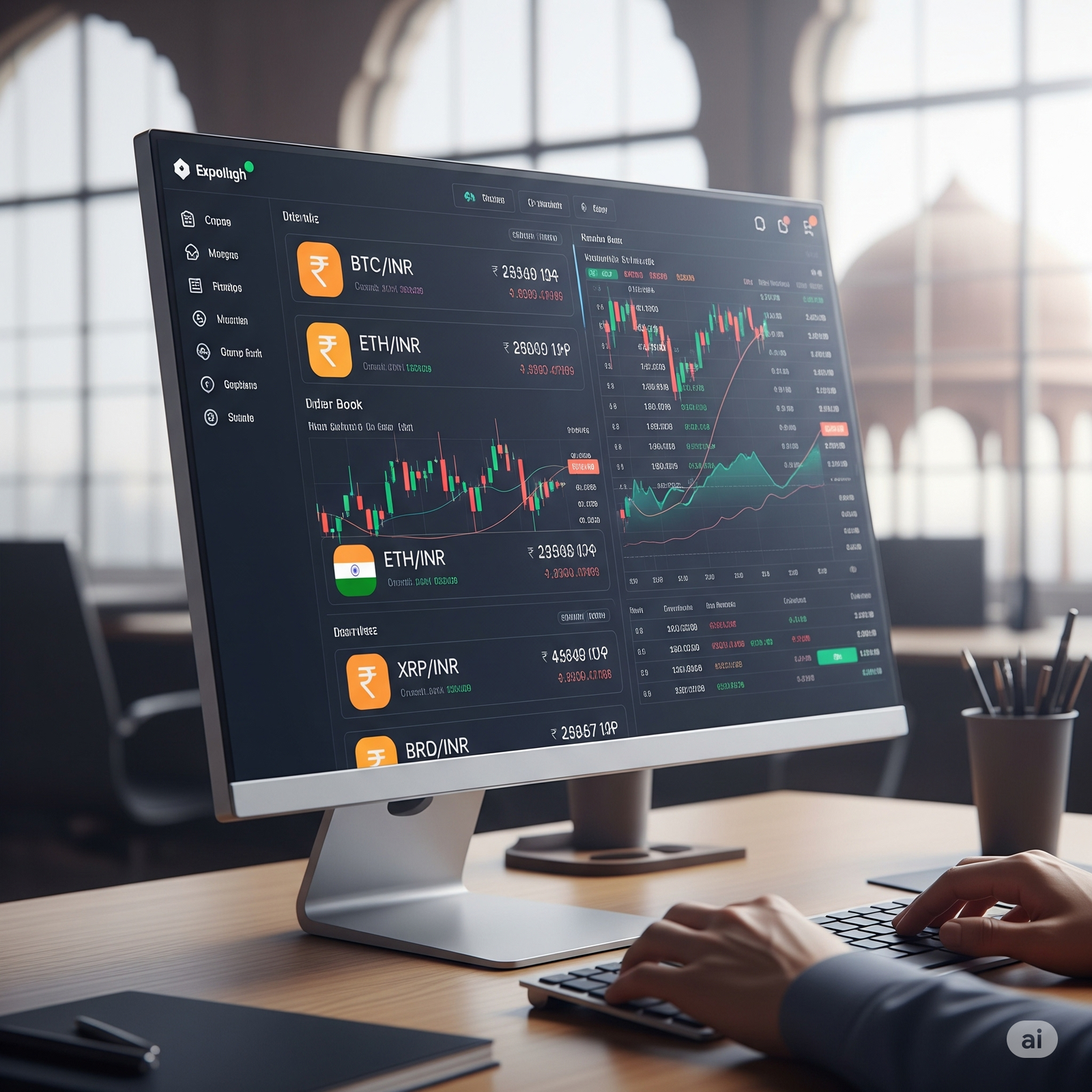
Exchanges provide an order book, which lists all the outstanding buy (bid) and sell (ask) orders for a particular cryptocurrency trading pair. Buyers look at the lowest ask prices, and sellers look at the highest bid prices. When a buy order matches a sell order at the same price, a trade is executed.
4. Order Execution and Matching:
The exchange’s trading engine is responsible for matching buy and sell orders. When a market order is placed, it’s immediately matched with the best available opposite order in the order book. For limit orders, the order will remain in the order book until a matching order is placed at the specified price.
5. Cryptocurrency Wallets:
Once you’ve bought cryptocurrencies, they are typically stored in a custodial wallet provided by the exchange. While convenient for trading, keeping your crypto on an exchange means you don’t have direct control over your private keys. For long-term storage and greater security, many users prefer to withdraw their crypto to their own non-custodial wallets, where they control their private keys.
6. Trading Pairs:
Cryptocurrencies are usually traded in pairs. For example, you might see a BTC/INR pair, which means you can buy or sell Bitcoin using Indian Rupees. Common trading pairs involve stablecoins (like USDT or USDC) or other major cryptocurrencies.
Key Features of Crypto Exchanges:
- User Interface: Exchanges offer trading platforms with charts, order books, and tools for analysis.
- Security Measures: Reputable exchanges implement various security measures, such as two-factor authentication (2FA), encryption, and cold storage of funds.
- Transaction Fees: Exchanges charge fees for trading, withdrawals, and sometimes deposits. These fees vary between exchanges.
- Customer Support: Most exchanges offer customer support channels to assist users with any issues.
Choosing a Crypto Exchange:
When selecting a crypto exchange, consider factors like:
- Security: Look for exchanges with strong security measures and a good track record.
- Fees: Compare the trading, deposit, and withdrawal fees.
- Supported Cryptocurrencies: Ensure the exchange offers the cryptocurrencies you are interested in trading.
- User Interface: Choose a platform that is user-friendly and easy to navigate.
- Regulation: Opt for exchanges that comply with local regulations.
- Customer Support: Check the availability and responsiveness of customer support.
In Conclusion:
Crypto exchanges serve as essential platforms for anyone looking to participate in the cryptocurrency market. By understanding how they work, from account creation to order execution and security measures, you can navigate this exciting space with greater confidence. Remember to always do your research and choose a reputable exchange that aligns with your trading needs and risk tolerance.











Leave a Reply